FATE Quality
These comments provided by Neurotechnology are based on NIST FATE Quality ongoing evaluation results reviewed on December 20, 2023.
NIST FATE Quality performs a series of tests to estimate the capability of image quality assessment algorithms to deal with face images captured in challenging photographic conditions. The tests first analyze specific metrics, like illumination, focus, or facial expressions. These metrics are used to assign quality values for facial images.
The FNMR values of a set of most accurate face verification algorithms from FRTE are then evaluated with a complete dataset of facial images, as well as after discarding 1% and 5% of the lowest quality images.
See FATE official page for more information.
Quality assessment algorithms (QAA) evaluate facial images based on various metrics, like pose, lighting, and resolution. QAA can falsely reject good images, or falsely accept bad ones, leading to recognition errors, which are increasing costs of operating facial recognition systems and reduce the overall system security. FATE Quality checks how QAA from different vendors handle with a method reminiscent of the NFIQ approach for fingerprints using machine learning.
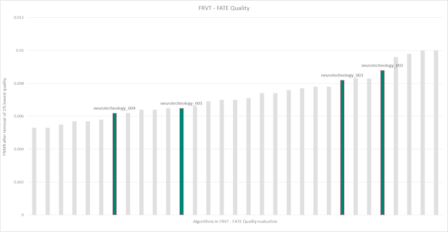
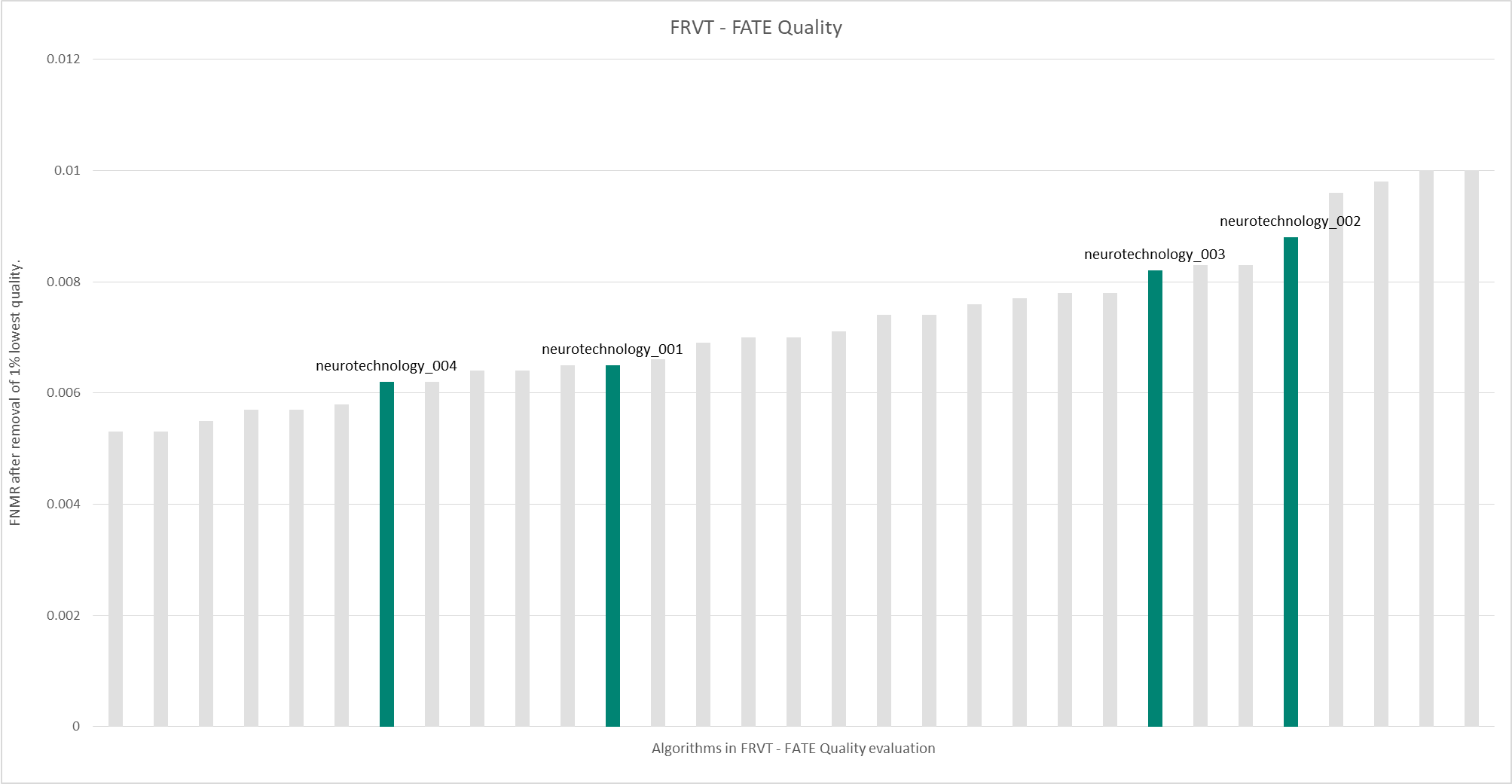
The testing scenario examined the impact of eliminating 1% and 5% of the poorest quality facial images, as determined by a QAA, on the false non-match rate (FNMR) of 15 facial recognition algorithms. The neurotechnology_004 algorithm submission showed these results in the testing scenario:
- 0.62% FNMR after removal of 1% lowest quality images. The most accurate contender showed 0.53% FNMR.
- 0.40% FNMR after removal of 5% lowest quality images. The most accurate contender showed 0.31% FNMR.
Click to zoom
Click to zoom