VeriEye SDK
Iris identification for stand-alone and client-server solutions
VeriEye iris identification technology is designed for biometric systems developers and integrators. The technology includes many proprietary solutions that enable robust iris enrollment under various conditions and fast iris matching in 1-to-1 and 1-to-many modes.
Available as a software development kit that allows development of stand-alone and network-based solutions on Microsoft Windows, Linux, macOS, iOS and Android platforms.
Features and Capabilities
- Rapid and accurate iris identification, proven by NIST IREX.
- Robust recognition, even with gazing-away eyes or narrowed eyelids.
- Original proprietary algorithm solves the limitations and drawbacks of existing state-of-the-art algorithms.
- Iris liveness detection can prevent spoof with fake iris images on photos or contact lenses.
- Available as multiplatform SDK that supports multiple programming languages.
- Programming samples and tutorials in C/C++, C#, VB .NET, Java and Python.
- Reasonable prices, flexible licensing and free customer support.
Click to zoom
Figure 2
Click to zoom
Figure 3
Click to zoom
Figure 4

Click to zoom
Figure 5
Click to zoom
Neurotechnology began research and development in the field of eye iris biometrics in 1994 and has released VeriEye iris recognition algorithm in 2008. The original proprietary algorithm solves the limitations and drawbacks of existing state-of-the-art algorithms. VeriEye implements advanced iris segmentation, enrollment and matching using robust digital image processing algorithms:
- Robust iris detection. Irises are detected even when there are obstructions to the image, visual noise and/or different levels of illumination. Lighting reflections, eyelids and eyelashes obstructions are eliminated. Images with narrowed eyelids or eyes that are gazing away are also accepted.
- Automatic interlacing detection and correction results in maximum quality of iris features templates from moving iris images.
- Gazing-away eyes are correctly detected on images, segmented and transformed as if it were looking directly into the camera (see Figure 1).
-
Correct iris segmentation is obtained even under these conditions:
- Perfect circles fail. VeriEye uses active shape models that more precisely model the contours of the eye, as iris boundaries are not modeled by perfect circles.
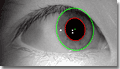
- The centers of the iris inner and outer boundaries are different (see Figure 2). The iris inner boundary and its center are marked in red, the iris outer boundary and its center are marked in green.
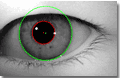
- Iris boundaries are definitely not circles and even not ellipses (see Figure 3) and especially in gazing-away iris images.
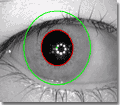
- Iris boundaries seem to be perfect circles. The recognition quality can still be improved if boundaries are found more precisely (see Figure 4). Note these slight imperfections when compared to perfect circular white contours.
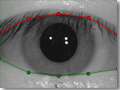
- Iris is partially occluded by eyelids. The upper and lower lids are marked in red and green correspondingly (see Figure 5).
- Iris image quality determination. The image quality estimation can be used during iris enrollment to ensure that only the best quality iris template will be stored into database. Roll angle can be determined from iris image for further decisions about accepting the image for enrollment. Also, irises, which are obscured by cosmetic (decorative) contact lenses with some artistic images or color change, can be rejected from enrollment.
- Liveness detection. A captured iris can be analyzed whether it is "live" or a spoof to prevent security breach performed by placing a photo in front of the camera or wearing contact lenses with fake iris texture.
- Automatic iris position detection. The algorithm is able to separate images of left and right irises.
- Reliability. VeriEye algorithm has shown excellent recognition accuracy during the NIST IREX evaluations.
All presented iris images are taken from CASIA Iris Image Database V2.0 and CASIA Iris Image Database V3.0 collected by the Chinese Academy of Sciences Institute of Automation (CASIA) (www.cbsr.ia.ac.cn/english/IrisDatabases.asp).
