FRTE Face Masks Effects
These comments provided by Neurotechnology are based on NIST FRTE Face Mask Effects ongoing evaluation results reviewed on December 20, 2023.
What is FRTE Face Mask Effects evaluation?
NIST FRTE Face Mask Effects evaluation addresses the real-world need to perform biometric facial recognition on persons wearing face masks, respirators, or other safety measures. One testing scenario compares faces occluded with face masks against non-occluded faces. Another scenario is a baseline comparison of non-occluded faces using the same datasets as in the first scenario. Various situations, such as medical environments, labs, pollution-heavy areas, or government-issued requirements underline the significance of recognizing occluded faces.
See FRTE official page for more information.
NIST FRTE Face Mask Effects evaluation addresses the real-world need to perform biometric facial recognition on persons wearing face masks, respirators, or other safety measures. One testing scenario compares faces occluded with face masks against non-occluded faces. Another scenario is a baseline comparison of non-occluded faces using the same datasets as in the first scenario. Various situations, such as medical environments, labs, pollution-heavy areas, or government-issued requirements underline the significance of recognizing occluded faces.
See FRTE official page for more information.
Neurotechnology's algorithm ranked as:
- third most accurate in the scenario, which matched images with subjects wearing face masks against previously captured images with non-occluded faces;
- top 5% for the scenario with baseline comparison between non-occluded faces.
There was a total of 263 algorithm submissions from different vendors.
Before July, 2023, this evaluation was called FRVT Face Mask Effects. Neurotechnology's submission reached the top 3% accuracy ranking there.
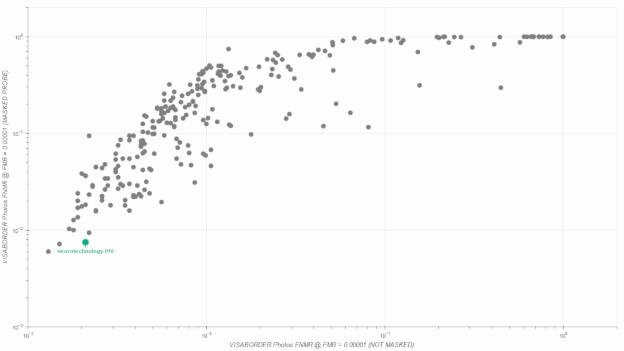
Visa vs Border, Masked Probe scenario
- One original image from the VISA dataset was used to create one face template.
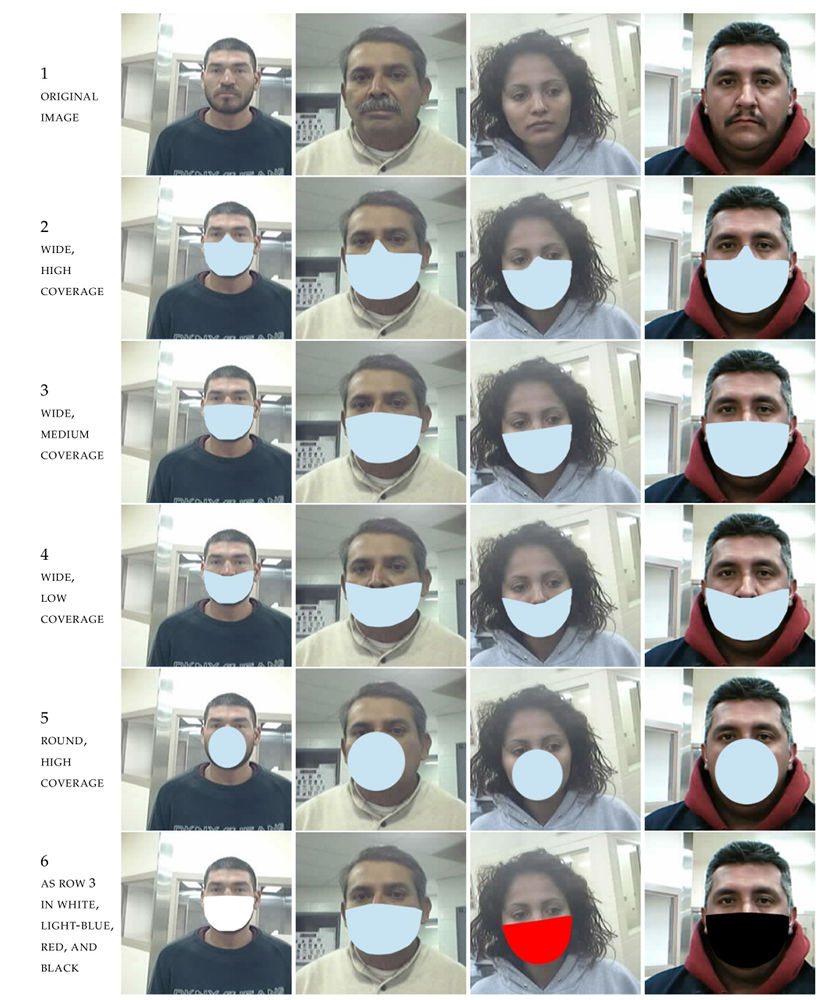
- Each original image from the BORDER dataset was post-processed in five different ways to create synthetic lower face part occlusions as if the subjects wear face masks (see the figure below). One face template was created from each variant of the modified image.
- Gender attribute was used to exclude comparisons between different gender subjects.
- Each pre-filtered template from the VISA dataset was compared against each pre-filtered template from the BORDER dataset with synthetic face masks.
- Each comparison score was obtained by comparing two different templates (simple one-to-one verification).
- Neurotechnology algorithm accuracy in this scenario was 0.75% FNMR at 0.0001% FMR.
- The most accurate contender showed 0.60% FNMR at the same FMR.
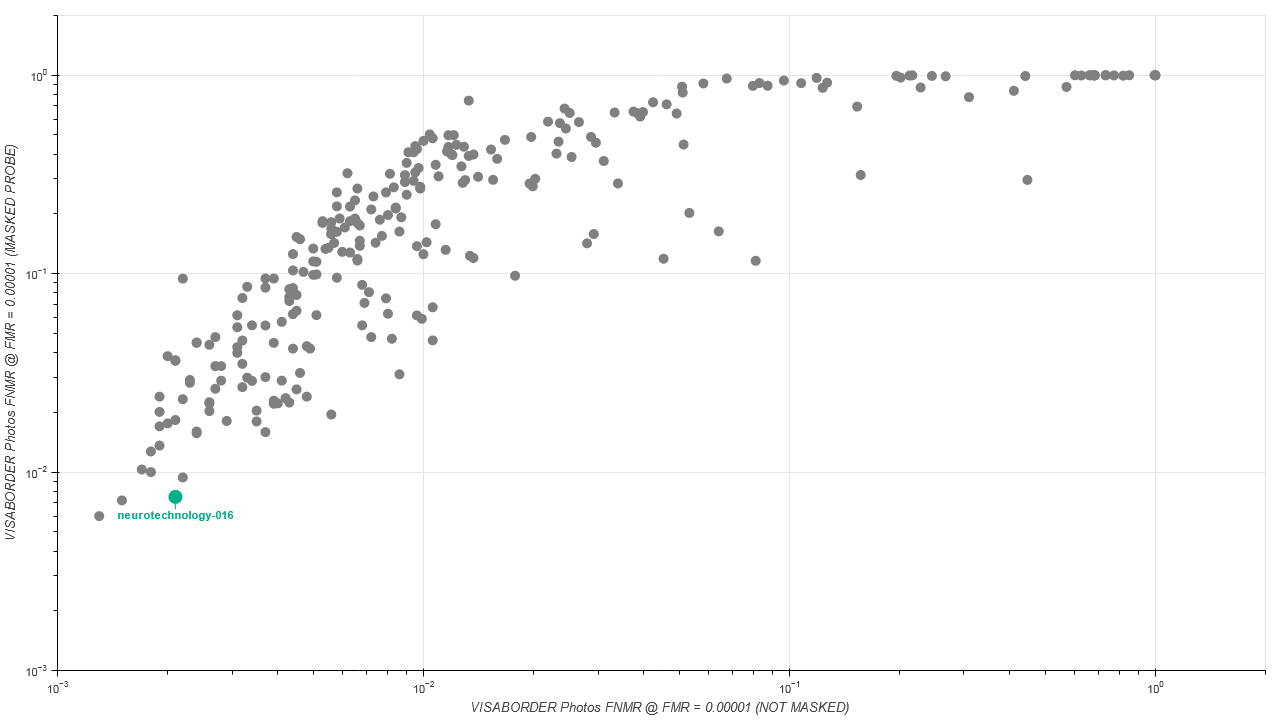
Visa vs Border, Not Masked scenario
- One image from Visa or Border datasets was used to create one face template.
- Gender attribute was used to exclude comparisons between different gender subjects.
- Each pre-filtered template from the Visa dataset was compared against each pre-filtered template from the Border dataset
- Each comparison score was obtained by comparing two different templates (simple one-to-one verification).
- Neurotechnology algorithm accuracy in this scenario was 0.21% FNMR at 0.0001% FMR.
- The most accurate contender showed 0.13% FNMR at the same FMR.
Datasets summary
-
VISA dataset
- More than 100,000 unique persons.
- Part of the images are live capture and part are digitized paper photos.
- High quality images, with conformance with the ISO/IEC 19794-5 Full Frontal image type. Subjects' pose is generally excellent.
- Image size: 252x300 pixels.
- Interocular distance (IOD): 69 pixels.
- Subjects from more than 100 countries are represented, with significant imbalance due to visa issuance patterns.
- All ages are represented, including children, with imbalance due to visa issuance demand.
-
BORDER dataset
- More than 1,000,000 unique persons.
- All images were live capture
- Variable image quality. There are role, pitch and yaw angle variations. There is some perspective distortion due to close range images. Background illumination is sometimes strong, so faces may be under-exposed. Some faces are partially cropped.
- Interocular distance (IOD): 38 pixels mean.
- Subjects from more than 100 countries are represented, with significant imbalance due to immigration patterns.
- All subjects are adults, with age distribution imbalance due to immigration patterns.
Awards Overview